Ever stepped on the scale and wondered what that number truly represents? You’re not alone. Our weight is a constant companion, but deciphering its deeper meaning can be a confusing journey. This is where the concept of BMI, or Body Mass Index, steps in. But what exactly is BMI meaning, and how can it help us understand our health?
This comprehensive guide will be your decoder ring, unlocking the secrets behind BMI. We’ll delve into its calculation, explore its limitations, and equip you with the knowledge to interpret your own BMI effectively. So, buckle up and get ready to crack the code of BMI meaning – it’s time to move beyond just a number on the scale!
Table of Contents
Understanding the BMI Meaning
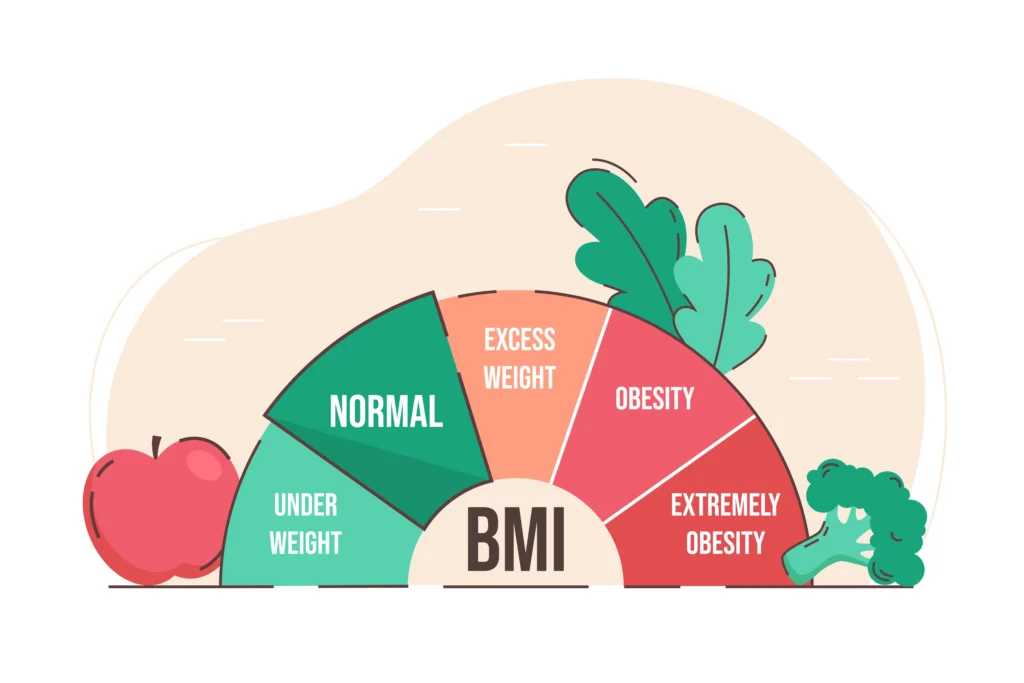
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a simple measure of body weight for height. It is used to categorize people into underweight, normal weight, overweight, and obese. While it’s a widely used tool, it’s important to understand its limitations.
BMI is calculated by dividing a person’s weight in kilograms by the square of their height in meters. The formula is:
BMI = weight (kg) / height (m)^2
Based on the calculated BMI, individuals are categorized as follows:
- Underweight: BMI less than 18.5
- Normal weight: BMI between 18.5 and 24.9
- Overweight: BMI between 25 and 29.9
- Obesity: BMI of 30 or greater
It’s crucial to note that BMI has its limitations. It doesn’t differentiate between muscle mass and fat, which can lead to inaccurate assessments for athletes or muscular individuals. Additionally, BMI might not accurately reflect health risks for all populations, such as older adults or certain ethnic groups. Therefore, it’s essential to use BMI as a screening tool rather than a definitive diagnostic tool.
Health Risks Associated with High BMI
Carrying excess weight, often indicated by a high BMI, is linked to a range of serious health problems.
Increased Risk of Chronic Diseases
High BMI significantly increases the risk of developing chronic conditions such as:
- Type 2 diabetes: Excess body fat can interfere with the body’s ability to use insulin effectively.
- Cardiovascular diseases: Heart disease, stroke, and high blood pressure are closely linked to obesity.
- Certain cancers: Some types of cancer, including breast, colon, and endometrial, are more common in individuals with higher BMI.
Impact on Quality of Life
Beyond the physical health risks, obesity can also negatively impact overall quality of life:
- Physical limitations: Excess weight can lead to reduced mobility, joint pain, and difficulty with daily activities.
- Psychological effects: Obesity is often associated with emotional challenges such as depression, anxiety, and low self-esteem.
- Social stigma and discrimination: Individuals with obesity may face prejudice and discrimination in various aspects of life.
Introduction to Bariatric Surgery
Bariatric surgery, also known as weight-loss surgery, is a procedure performed on the stomach and intestines to help people with severe obesity lose weight and improve their health. It is considered a last resort after other weight loss methods, such as diet and exercise, have failed.
There are several types of bariatric surgery, each with its own benefits, risks, and suitability for different individuals.
Gastric Bypass
Gastric bypass is the most common type of bariatric surgery. It involves creating a small pouch in the upper part of the stomach and bypassing a portion of the small intestine. This significantly reduces food intake and absorption.
- How it works: The surgeon creates a small pouch at the top of the stomach, and then connects it directly to the lower part of the small intestine. This restricts food intake and limits the body’s ability to absorb calories.
- Suitable BMI: Typically, a BMI of 40 or higher, or a BMI of 35 or higher with obesity-related health conditions.
Sleeve Gastrectomy
A sleeve gastrectomy involves removing about 80% of the stomach, creating a tube-shaped or “sleeve” stomach. This reduces the amount of food the stomach can hold and leads to weight loss.
- How it works: The surgeon removes a large portion of the stomach, leaving a smaller, banana-shaped stomach. This restricts food intake and reduces the production of hunger hormones.
- Suitable BMI: Typically, a BMI of 35 or higher with obesity-related health conditions.
Adjustable Gastric Band
An adjustable gastric band is a silicone band placed around the upper part of the stomach, creating a small pouch. The band can be adjusted to control the amount of food that passes through to the rest of the stomach.
- How it works: The band creates a smaller upper stomach pouch, restricting food intake. The tightness of the band can be adjusted to control the size of the opening.
- Suitable BMI: Generally, a BMI of 30 or higher with obesity-related health conditions.
Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch (BPD/DS)
This complex procedure involves both restrictive and malabsorptive elements. A large portion of the stomach is removed, and the small intestine is rearranged.
- How it works: The surgery involves creating a small stomach pouch, bypassing a significant portion of the small intestine, and reconnecting the remaining intestine to the stomach. This restricts food intake and reduces calorie absorption.
- Suitable BMI: Typically reserved for patients with extreme obesity (BMI of 50 or higher) and who have failed other weight loss surgeries.
Important note: The ideal type of bariatric surgery for each individual depends on various factors, including BMI, overall health, and personal preferences. It is crucial to consult with a qualified bariatric surgeon to determine the best option.
Gastric Plication
Gastric plication is a relatively new type of bariatric surgery that involves folding and suturing a portion of the stomach to create a series of pleats. This reduces the stomach’s volume, limiting food intake and promoting satiety.
- How it works: The surgeon makes folds in the stomach wall and sutures them together, creating a smaller stomach pouch. This restricts the amount of food that can fit in the stomach, leading to feelings of fullness sooner.
- Suitable BMI: While gastric plication is still under research, it may be a suitable option for individuals with a BMI of 30-40 or those who are not eligible for other bariatric surgeries due to health risks.
How Bariatric Surgery Helps with Weight Loss
Bariatric surgery aids weight loss through a combination of factors:
Mechanisms of Weight Loss
- Restriction: Most procedures reduce the stomach’s capacity, limiting the amount of food that can be consumed at one time. This leads to feeling fuller sooner and eating less overall.
- Malabsorption: Some surgeries, such as gastric bypass and biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch, alter the digestive process, reducing the body’s ability to absorb nutrients and calories.
- Hormonal changes: Bariatric surgery can influence the production of hormones related to hunger and satiety. These changes help regulate appetite and promote weight loss.
Expected Weight Loss Outcomes
The amount of weight loss varies depending on the type of surgery, individual factors, and adherence to post-operative guidelines. Generally, individuals can expect:
- Typical weight loss percentages: Most people lose a significant amount of weight within the first year to two years after surgery. Weight loss typically ranges from 50% to 80% of excess body weight.
- Long-term weight maintenance: While initial weight loss is impressive, maintaining the weight loss long-term requires ongoing lifestyle changes, including healthy eating, regular exercise, and medical follow-up.
It’s important to note that bariatric surgery is a tool to aid weight loss, but it’s not a magic solution. Sustained weight loss and improved health require commitment and dedication to a healthier lifestyle.
Safety and Risks of Bariatric Surgery
While bariatric surgery offers significant benefits, it’s essential to understand the potential risks and complications. Careful preoperative evaluation and preparation, as well as diligent post-operative care, can help minimize these risks.
Preoperative Assessments and Preparation
To ensure patient safety and optimal outcomes, a comprehensive evaluation is conducted before surgery. This typically includes:
- Medical evaluations: Assessing overall health, including heart, lung, and liver function, to identify any underlying conditions that may impact surgery.
- Psychological assessments: Evaluating the patient’s emotional state, motivation for weight loss, and ability to cope with the surgery and its aftermath.
- Nutritional counseling: Providing guidance on pre-surgery diet and preparing the body for the changes after surgery.
Potential Risks and Complications
As with any major surgery, there are potential risks and complications associated with bariatric surgery. These can include:
- Surgical risks: Infection, bleeding, blood clots, anesthesia complications, and reactions to medications.
- Nutritional deficiencies: Malabsorption can lead to deficiencies in vitamins and minerals, requiring lifelong supplementation.
- Need for lifestyle changes: Successful long-term weight management necessitates significant adjustments to diet and exercise habits.
How to Avoid Risks and Side Effects
Several factors contribute to minimizing risks and optimizing outcomes:
- Minimally invasive solutions: Laparoscopic and robotic techniques often reduce surgical trauma and recovery time.
- Choosing the right surgeon: Selecting a highly experienced and qualified bariatric surgeon is crucial.
- Importance of follow-up care: Regular medical check-ups, attending support groups, and adhering to dietary and exercise recommendations are essential for long-term success.
By carefully considering the potential risks and benefits, patients can make informed decisions about whether bariatric surgery is the right choice for them.
In Summary
BMI, while not a perfect measure, serves as a valuable tool for assessing weight-related health risks. A high BMI is strongly linked to chronic diseases, reduced quality of life, and increased mortality. For individuals struggling with severe obesity, bariatric surgery can be a safe and effective option for significant weight loss and improved health.
It’s crucial to remember that bariatric surgery is not a miracle cure. Long-term success depends on a comprehensive approach that includes careful preoperative evaluation, experienced surgical care, and a dedicated commitment to post-operative lifestyle changes. This involves adopting healthy eating habits, engaging in regular physical activity, and attending follow-up appointments.
While bariatric surgery offers a powerful tool for weight management, it’s essential to consult with healthcare professionals to determine the best approach for individual circumstances. By understanding the risks and benefits and working closely with a medical team, individuals can make informed decisions about their weight loss journey.

